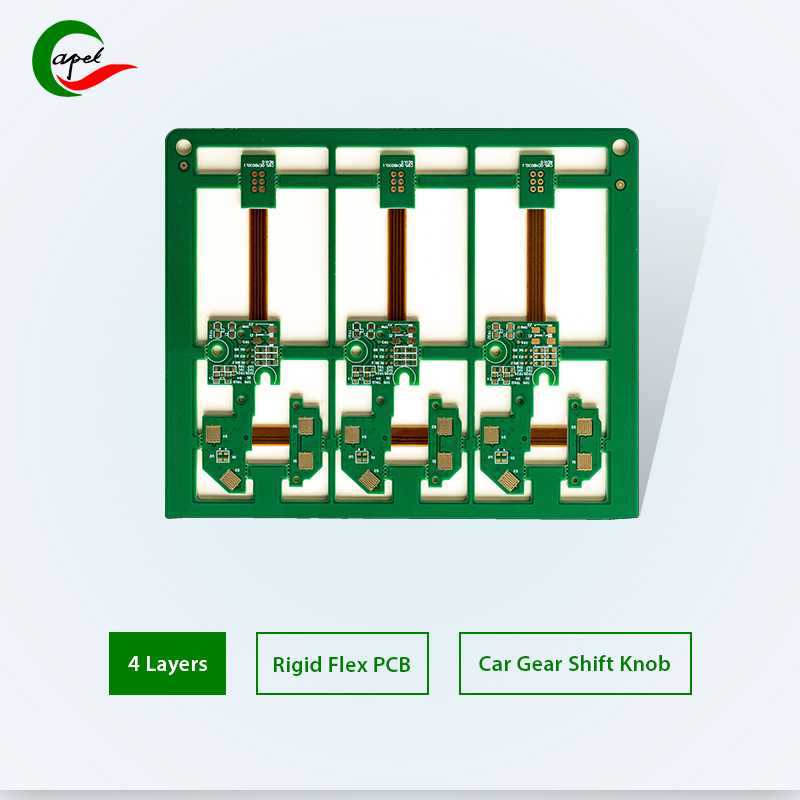
Specification
| Category | Process Capability | Category | Process Capability |
| Production Type | Single layer FPC / Double layers FPC Multi- layer FPC / Aluminum PCBs Rigid-Flex PCB | Layers Number | 1-16 layers FPC 2-16 layers Rigid-FlexPCB HDI Boards |
| Max Manufacture Size | Single layer FPC 4000mm Doulbe layers FPC 1200mm Multi-layers FPC 750mm Rigid-Flex PCB 750mm | Insulating Layer Thickness | 27.5um /37.5/ 50um /65/ 75um / 100um / 125um / 150um |
| Board Thickness | FPC 0.06mm - 0.4mm Rigid-Flex PCB 0.25 - 6.0mm | Tolerance of PTH Size | ±0.075mm |
| Surface Finish | Immersion Gold/Immersion Silver/Gold Plating/Tin Plat ing/OSP | Stiffener | FR4 / PI / PET / SUS / PSA/Alu |
| Semicircle Orifice Size | Min 0.4mm | Min Line Space/ width | 0.045mm/0.045mm |
| Thickness Tolerance | ±0.03mm | Impedance | 50Ω-120Ω |
| Copper Foil Thickness | 9um/12um / 18um / 35um / 70um/100um | Impedance Controlled Tolerance | ±10% |
| Tolerance of NPTH Size | ±0.05mm | The Min Flush Width | 0.80mm |
| Min Via Hole | 0.1mm | Implement Standard | GB / IPC-650 / IPC-6012 / IPC-6013II / IPC-6013III |
We do Rigid-Flexible Circuit Boards with 15 years' experience with our professionalism
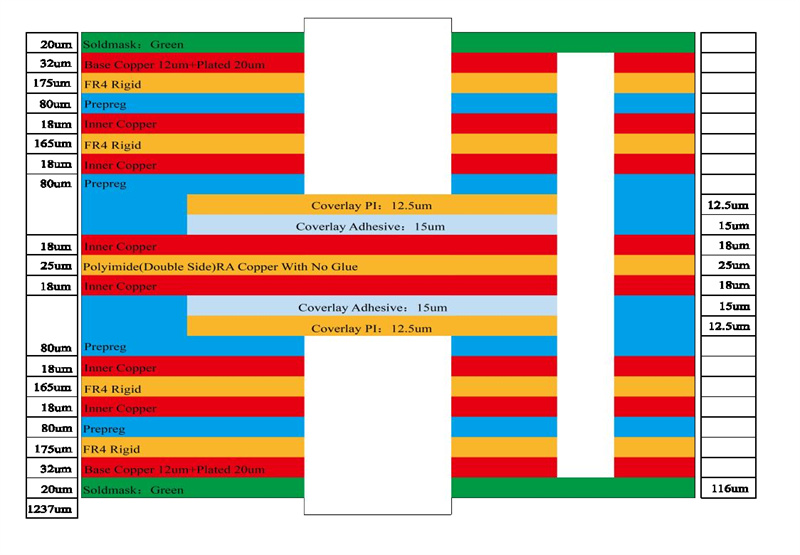
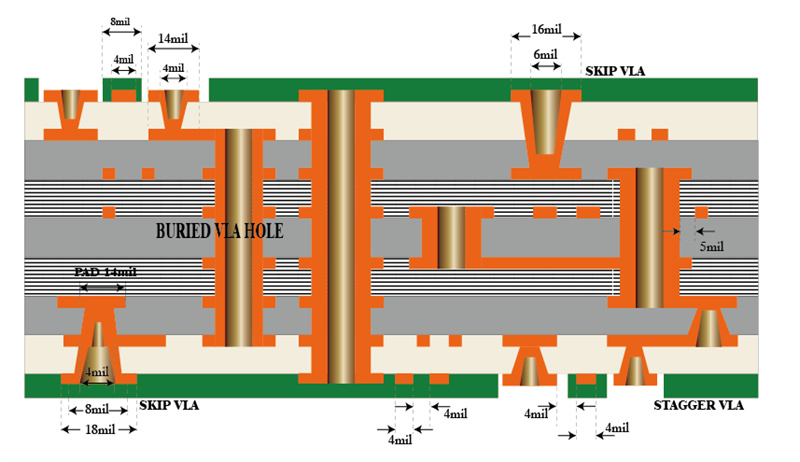


8 layer HDI PCBs
5 layer Flex-Rigid Boards
8 layer Rigid-Flex PCBs
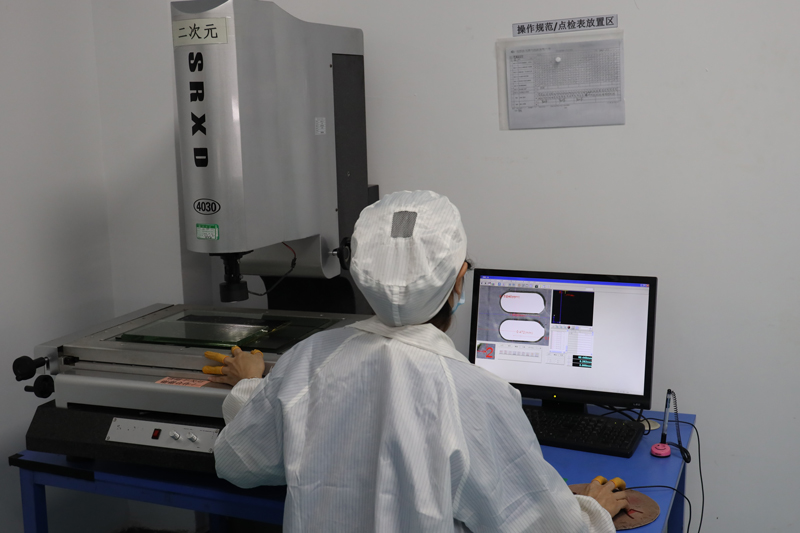
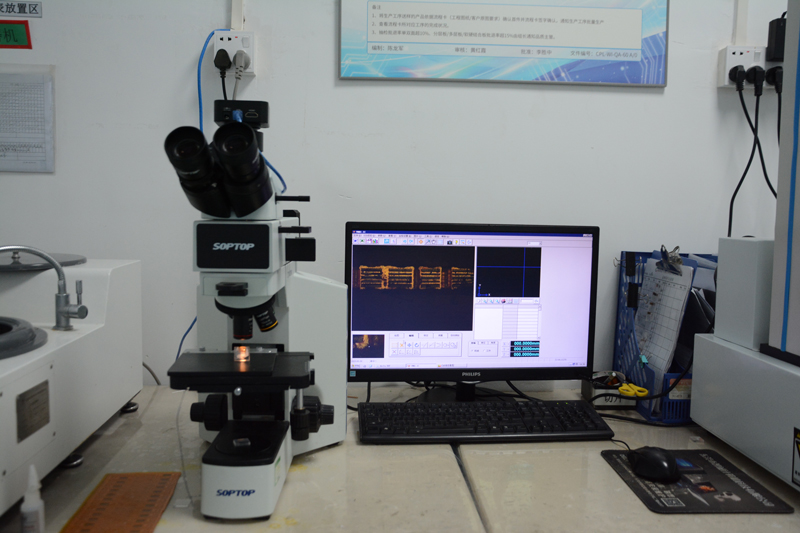
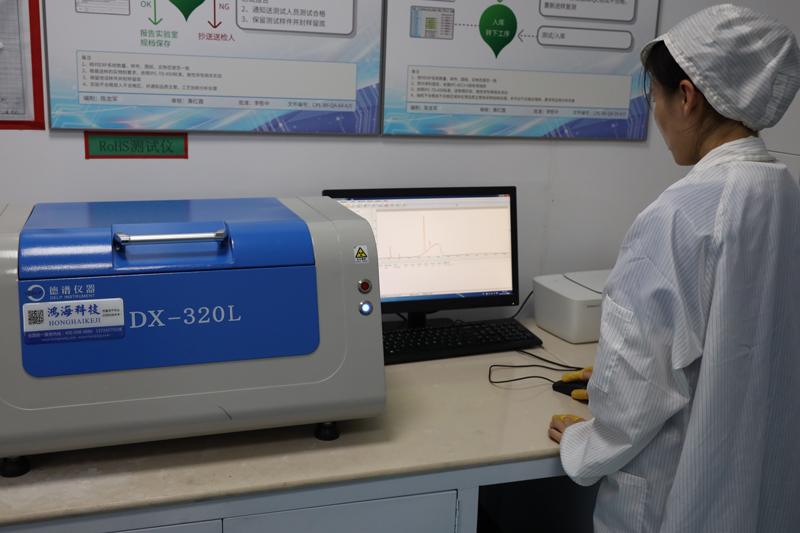
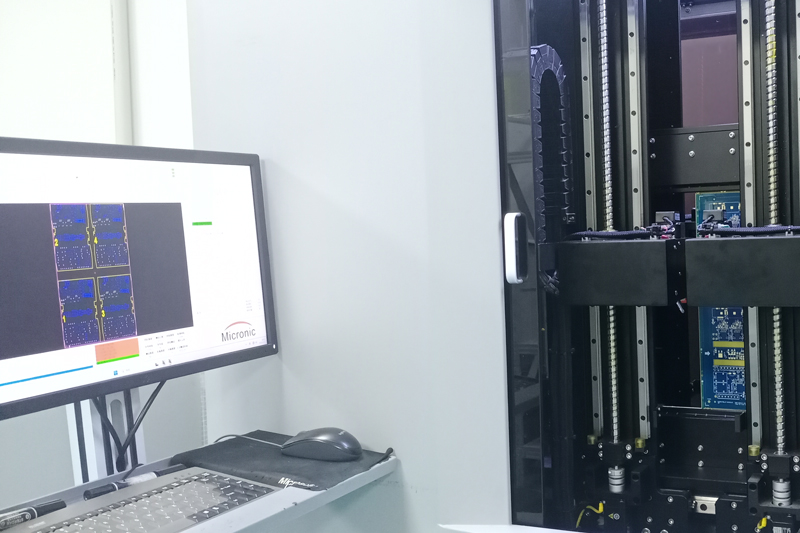
Testing and Inspection Equipment
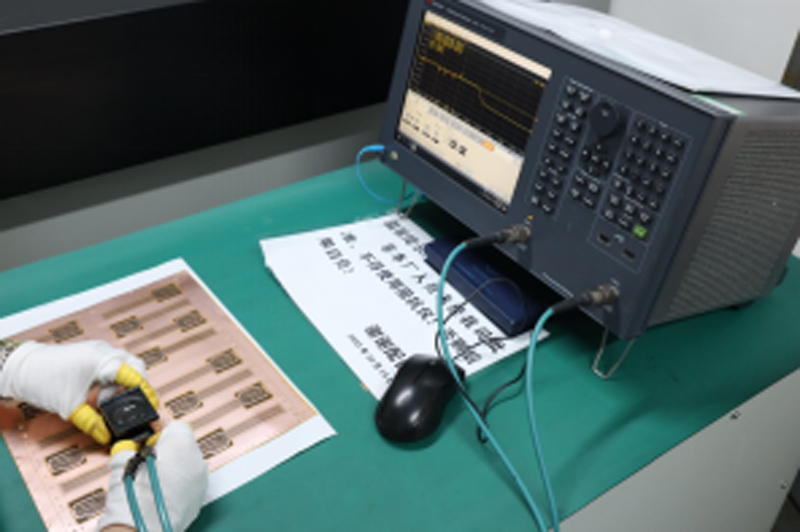
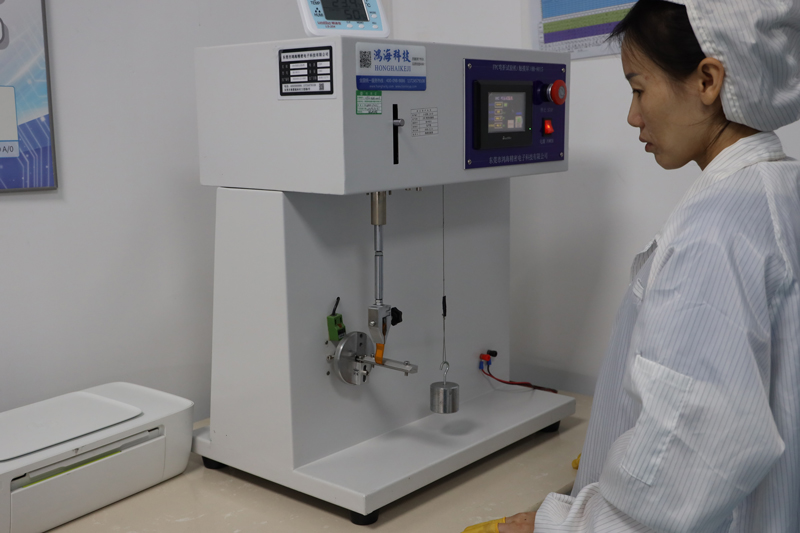
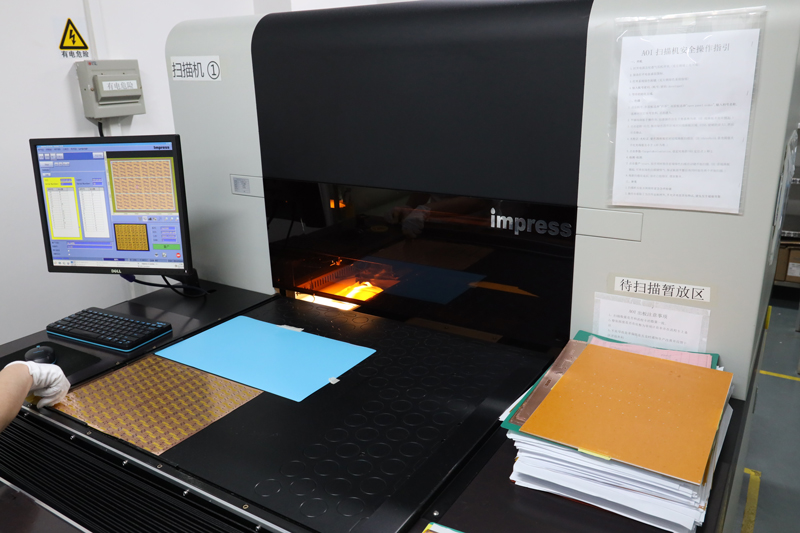







what we will consider when custom PCBs for Medical Device
. Provide technical support Pre-sales and after-sales; . Custom up to 40 layers, 1-2days Quick turn reliable prototyping, Component procurement, SMT Assembly; . Caters to both Medical Device, Industrial Control, Automotive, Aviation, Consumer Electronics, IOT, UAV, Communications etc.. . Our teams of engineers and researchers are dedicated to fulfilling your requirements with precision and professionalism.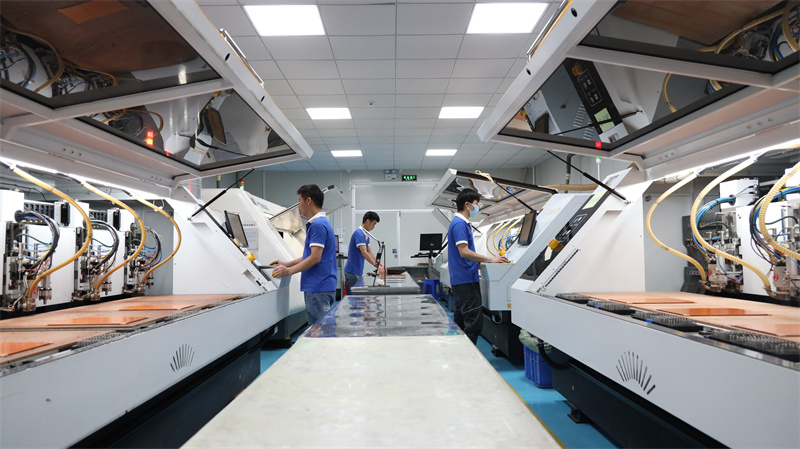
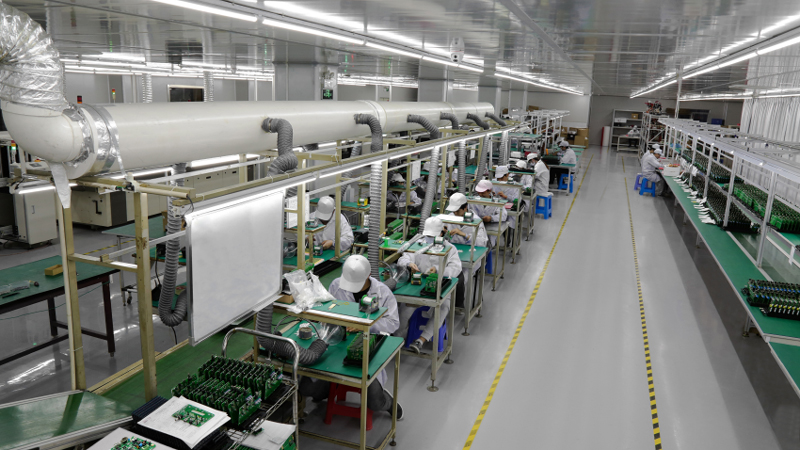
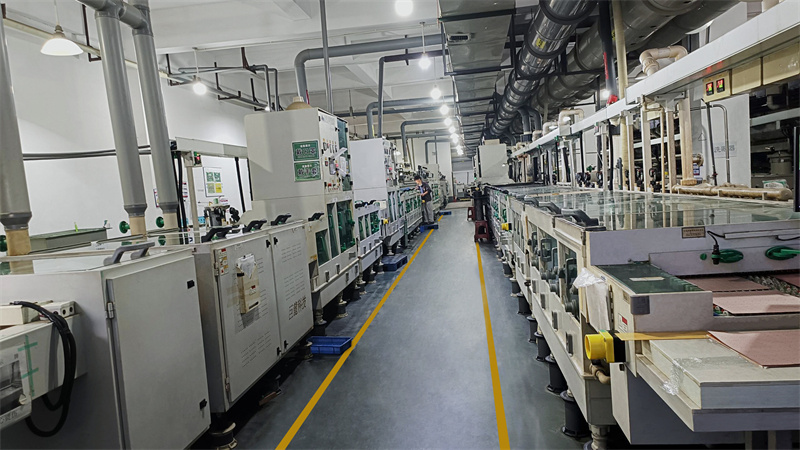



Our Rigid-Flexible Circuit Boards Service
1. Safety: Medical devices must comply with strict safety standards. Ensure that the PCB design complies with all applicable safety regulations such as IEC 60601-1. Implement features such as isolation barriers, proper grounding, and protection against electrical hazards. 2. Reliability: Medical devices need to perform flawlessly and consistently. Consider using high-quality components with a proven track record. Extensive reliability testing, such as environmental testing, is performed to ensure that the PCB can withstand expected conditions. 3. EMI/EMC: Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) can interfere with the proper operation of medical devices and affect patient safety. Implement techniques such as proper grounding, shielding, and isolation to minimize EMI/EMC issues. 4. Size constraints: Medical devices often need to be portable or compact. Consider size constraints when designing the PCB. Utilize surface mount technology (SMT), miniaturized components, and efficient layout techniques to optimize space utilization. 5. Power management: Medical devices may have specific power requirements, such as requiring battery operation or low power consumption. Optimize power distribution networks, implement energy-saving technologies, and consider features such as sleep modes. 6. Sterilization compatibility: Some medical devices need to be sterilized before use. Ensure that PCB materials and components can withstand the chosen sterilization method, such as autoclaving, ethylene oxide (ETO) treatment, or gamma radiation. 7. Traceability and Documentation: Documentation plays a vital role in the medical device industry. Maintain comprehensive and accurate records including bill of materials (BOM), schematics, PCB fabrication details, and any changes made during the design process. 8. Support for future updates: Due to regulatory changes or functional improvements, medical devices may need to be updated or upgraded over time. Design the PCB with modularity and scalability in mind to facilitate future updates without a complete redesign. 9. Compliance: Ensure compliance with all relevant regulatory standards, such as FDA regulations or EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Comply with labeling guidelines, Unique Device Identification (UDI), and any other medical device-specific requirements. 10. Collaborate with experts: Involve experts in the medical field, including clinicians and regulatory experts, in the design process. Solicit their input and feedback to ensure that the PCB design meets the specific needs and requirements of the medical device.
5. Power management: Medical devices may have specific power requirements, such as requiring battery operation or low power consumption. Optimize power distribution networks, implement energy-saving technologies, and consider features such as sleep modes. 6. Sterilization compatibility: Some medical devices need to be sterilized before use. Ensure that PCB materials and components can withstand the chosen sterilization method, such as autoclaving, ethylene oxide (ETO) treatment, or gamma radiation. 7. Traceability and Documentation: Documentation plays a vital role in the medical device industry. Maintain comprehensive and accurate records including bill of materials (BOM), schematics, PCB fabrication details, and any changes made during the design process. 8. Support for future updates: Due to regulatory changes or functional improvements, medical devices may need to be updated or upgraded over time. Design the PCB with modularity and scalability in mind to facilitate future updates without a complete redesign. 9. Compliance: Ensure compliance with all relevant regulatory standards, such as FDA regulations or EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR). Comply with labeling guidelines, Unique Device Identification (UDI), and any other medical device-specific requirements. 10. Collaborate with experts: Involve experts in the medical field, including clinicians and regulatory experts, in the design process. Solicit their input and feedback to ensure that the PCB design meets the specific needs and requirements of the medical device. Rigid-Flexible Circuit Boards for Medical Device FQA
1. What are the advantages of using rigid-flex boards for medical devices? - Rigid-flex boards offer space-saving designs, increased reliability, flexibility and bendability. - Their durability and resistance to environmental factors make them suitable for use in medical devices. - Rigid-flex boards also provide compatibility with sterilization methods and facilitate traceability and labeling requirements. 2. Are rigid-flex circuit boards suitable for implantable medical devices? - Yes, rigid-flex boards can be used in implantable medical devices. However, materials and components must be selected to meet biocompatibility requirements, taking into account the long-term performance and safety of the implanted device. 3. Can rigid-flex circuit boards withstand the sterilization process? - Yes, rigid-flex boards can withstand sterilization processes such as autoclaving, ethylene oxide, or radiation. Selecting materials and components that are compatible with the specific sterilization method required for a medical device is critical. 4. What are the key considerations for selecting materials for rigid-flex circuit boards in medical devices? - Material selection should focus on biocompatibility, durability, resistance to environmental factors, and compatibility with sterilization methods. - High-quality polymers, such as polyimide or silicone, are usually used for flexible parts, while rigid parts are usually made of FR-4 or other rigid PCB materials. 5. How can EMI/RFI shielding be incorporated into a rigid-flex circuit board? - EMI/RFI shielding can be achieved by placing sensitive components within grounded rigid sections or by adding conductive foil or mesh layers to flexible sections. These shields help prevent electromagnetic or radio frequency interference. 6. Are there any specific standards or regulations to consider when designing rigid-flex circuit boards for medical devices? - Yes, medical devices must comply with relevant standards and regulations such as ISO 13485 for quality management and IEC 60601 for electrical safety. It is important to work with an experienced manufacturer who understands these standards to ensure compliance. 7. How to ensure the reliability of rigid-flex circuit boards in medical devices? - Thorough testing and validation, including electrical testing, environmental testing, and usability testing, should be performed to ensure the reliability and performance of rigid-flex boards in medical equipment.
4. What are the key considerations for selecting materials for rigid-flex circuit boards in medical devices? - Material selection should focus on biocompatibility, durability, resistance to environmental factors, and compatibility with sterilization methods. - High-quality polymers, such as polyimide or silicone, are usually used for flexible parts, while rigid parts are usually made of FR-4 or other rigid PCB materials. 5. How can EMI/RFI shielding be incorporated into a rigid-flex circuit board? - EMI/RFI shielding can be achieved by placing sensitive components within grounded rigid sections or by adding conductive foil or mesh layers to flexible sections. These shields help prevent electromagnetic or radio frequency interference. 6. Are there any specific standards or regulations to consider when designing rigid-flex circuit boards for medical devices? - Yes, medical devices must comply with relevant standards and regulations such as ISO 13485 for quality management and IEC 60601 for electrical safety. It is important to work with an experienced manufacturer who understands these standards to ensure compliance. 7. How to ensure the reliability of rigid-flex circuit boards in medical devices? - Thorough testing and validation, including electrical testing, environmental testing, and usability testing, should be performed to ensure the reliability and performance of rigid-flex boards in medical equipment.